Burns are among the most common household injuries, yet they can be incredibly serious if not treated correctly and promptly. Understanding how to administer effective First Aid for Burns can make a significant difference in the outcome, potentially saving lives and reducing long-term damage.
At Lightning Training Solutions, we are dedicated to equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to handle such emergencies confidently and competently.
In this blog post, we will explore the essential steps for providing First Aid to anyone who has suffered a burn, helping you act quickly and effectively in an emergency.
Whether you’re at home, at work, or out and about, knowing how to respond to burns can make all the difference. Join us as we delve into the types, causes, and immediate First Aid techniques that can help mitigate the impact of burn injuries.
Understanding Burns
Types of Burns
Burns are classified into three main categories based on their severity:
Superficial (1st degree burns)
First-degree burns affect only the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). They usually cause redness, minor swelling, and pain. Sunburns are a common example of first-degree burns.
Partial Thickness (2nd degree burns)
Second-degree burns involve both the outer layer and the underlying layer of skin (dermis). They result in blisters, severe pain, and redness. These burns may also cause the skin to appear wet or shiny.
Full Thickness (3rd degree burns)
Third-degree burns penetrate all layers of the skin and can affect tissues beneath, such as muscles and bones. The burned area may appear white, blackened, or charred. Surprisingly, these burns may not be painful initially due to nerve damage.
| TYPE | CAUSE |
|---|---|
| Scald | Steam / Hot Liquid |
| Dry | Iron / Fire |
| Electrical | Electricity |
| Chemical | Chemicals |
| Radiation | Sunshine / Sunbeds |
| Cold | Ice |
“In the UK, there are over 130,000 burns and scalds attended to in hospitals every year.”
Source: NHS Digital, ‘Hospital Episode Statistics, Admitted Patient Care – England, 2019-20′
Causes of Burns
Burns can occur from various sources, each requiring specific First Aid measures:
Thermal Burns
Thermal burns are caused by direct contact with heat sources such as fire, hot liquids, steam, or hot objects.

Chemical Burns
Chemical burns result from exposure to corrosive substances like acids, alkalis, or solvents. These burns can continue to damage the skin and tissues until the chemical is thoroughly washed away.
Electrical Burns
Electrical burns happen when an electric current passes through the body, causing internal and external injuries. These burns often have entry and exit wounds.
Radiation Burns
Radiation burns are caused by prolonged exposure to UV rays from the sun or other sources of radiation, such as X-rays or radiation therapy.
Understanding the types and causes of burns is crucial for administering the correct First Aid.
In the next section, we’ll discuss the immediate steps you should take when faced with a burn injury.
Treating Burns & Scalds in Children
Immediate Steps to Take for Burns
When a burn occurs, taking prompt action can significantly impact the severity of the injury and the speed of recovery. Here’s what you should do immediately:
Assess the Situation
Ensuring Personal Safety
Before administering First Aid to a burn victim, ensure that the area is safe for both you and the casualty. This may involve extinguishing flames, turning off electrical sources, or removing the person from the source of the burn.
Evaluating the Severity of the Burn
Assess the burn to determine its severity. This will guide you in providing the appropriate level of First Aid. Consider the size of the burn, the depth of the injury, and whether it affects sensitive areas such as the face, hands, feet, or genitals.
First Aid Steps
Cooling the Burn
- Cooling the Burn: Immediately cool the burned area with cool (not cold) running water for a minimum of 20 minutes. This helps to reduce the skin’s temperature and minimise damage. Avoid using ice or very cold water, as it can further damage the tissue.
- Remove Constrictive Items: If the burn is not severe and is located on an extremity, remove any jewellery or clothing that could constrict swelling once the area begins to swell.
Protecting the Burn
- Covering the Burn: Once cooled, cover the burn with a clean, non-stick dressing or cling film to protect it from infection. Avoid using adhesive dressings or creams, as these can further irritate the burn.
Avoiding Complications
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol or ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, always check with the casualty or a healthcare professional before administering medication.
By taking these immediate steps, you can provide crucial support to someone who has suffered a burn injury.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to escalate the care of a burn injury to medical professionals is crucial.
Here are the key factors to consider:
Criteria for Seeking Professional Help
Burns Covering Large Areas
- Extent: Burns that cover a large area of the body, typically larger than the palm of the casualty’s hand, may require medical assessment and treatment. These burns can lead to fluid loss, infection, and other complications.
Burns on Sensitive Areas
- Location: Burns on sensitive areas such as the face, hands, feet, genitals, or major joints require professional evaluation. These areas are prone to complications and may require specialised care to minimise long-term damage.
Signs of Infection
- Symptoms: Watch for signs of infection such as increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth around the burn, or the presence of pus. These indicate that medical intervention is necessary to prevent further complications.
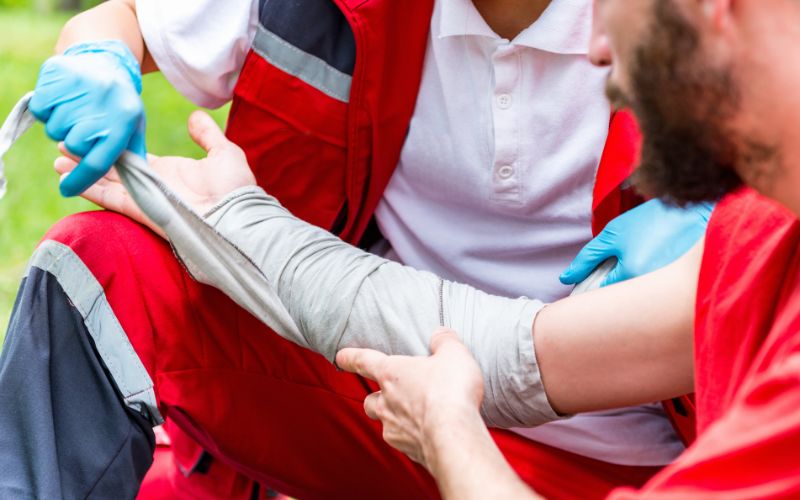

Emergency Situations
Severe Burns
- Severity: Burns that are deep, causing white or charred skin, or that appear leathery and dry may indicate third-degree burns. These require immediate medical attention due to the risk of extensive tissue damage and shock.
Electrical and Chemical Burns
- Nature of the Burn: Burns caused by electricity or corrosive chemicals can cause internal damage that may not be immediately visible. These injuries require a professional assessment to manage potential complications effectively.
Action Steps
- Prompt Action: If any of the above criteria are met or if you are unsure about the severity of the burn, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. Contact emergency services or take the casualty to the nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department for assessment and treatment.
Understanding when to seek medical attention for burns can ensure that appropriate care is provided in critical situations. In the following sections, we will explore practical tips for preventing burns and discuss the importance of First Aid training in handling such emergencies effectively.
Preventing Burns
Taking preventive measures is key to reducing the risk of burn injuries, both at home and in the workplace. Here are some practical tips to help prevent burns:
Home Safety Tips
Kitchen Safety
- Awareness: Always supervise cooking and never leave hot appliances or pans unattended on the stove.
- Handles: Turn pot handles towards the back of the stove to prevent accidental spills.
- Children: Keep children away from the stove and hot surfaces.
Electrical Safety
- Appliances: Regularly check electrical appliances for signs of damage or wear.
- Cords: Ensure cords are not frayed or placed near heat sources.
- Outlets: Avoid overloading electrical outlets and use surge protectors when necessary.
Workplace Safety Tips
Protective Gear
- Appropriate Clothing: When handling hot materials or chemicals, wear appropriate protective clothing, such as gloves and aprons.
- Training: Ensure all employees are trained in safe handling procedures for equipment and hazardous substances.
Safe Handling of Hazardous Materials
- Labels: Always read and follow the instructions and warnings on chemical containers.
- Ventilation: Use chemicals in well-ventilated areas to reduce the risk of inhalation and skin contact.
Why First Aid Training is Crucial
While prevention is essential, accidents can still happen. Being trained in Burns First Aid equips individuals with the skills and confidence to respond effectively in emergencies:
Benefits of Being Trained
- Confidence: Gain confidence in your ability to provide immediate assistance during a burn or any other emergency.
- Skill: Learn how to assess the situation, administer appropriate First Aid, and potentially save lives.
- Legal Requirements: In some workplaces, having employees trained in First Aid (not just burns) is a legal requirement to ensure safety and compliance.
How Lightning Training Solutions Can Help
Lightning Training Solutions offers comprehensive First Aid Training Courses designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to respond to emergencies confidently:
- Courses Explore our range of courses, including First Aid at Work, Emergency First Aid at Work, Refresher Courses and specialised training for handling burns and other injuries.
- Expertise: Benefit from our experienced instructors who provide practical, hands-on training in a supportive learning environment.
- Customisation: We can tailor training programmes to meet the specific needs of your workplace or organisation, ensuring relevance and effectiveness.
Final Thoughts
By implementing preventive measures and investing in First Aid training, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce the incidence and impact of burn injuries.
Remember, quick and effective action in the event of a burn can make a critical difference in the outcome of the casualty. Check out our huge range of courses today to discover how we can empower you with life-saving skills through our training programmes.
First Aid Courses & Price List
| Available Courses | Duration | Per Course | Per Person |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health & Safety First Aid at Work | 3 Days | £1,800 | *£180 |
| Health & Safety Emergency First Aid at Work | 1 Day | £700 | *£70 |
| First Aid at Work Re-Qualification Course | 2 Days | £1,200 | *£120 |
| Annual Refresher First Aid at Work Course | ½ Day | £300 | *£30 |
Please note: * Book a full course (12 places) and get 2 places FREE! (prices listed ‘per person’ reflect discount)
Each first aid course can accommodate a maximum of 12 people. However, we are always happy to accommodate any number of people your business may need to train, and prices for fewer numbers of people can be negotiated. Please contact us for details.
Prices Updated 01/03/2024: All prices are subject to VAT and may be updated without prior notice. Terms and Conditions apply.


The Quality Management system at FAIB holds 3rd Party Certification via a United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) Accredited Certification Body.